
- An if statement can be followed by an optional else if.else statement, which is very usefull to test various conditions using single if.else if statement. When using if, else if, else statements there are few points to keep in mind.
- Oct 29, 2020 Looping is one of the key concepts on any programming language. A block of looping statements in C are executed for number of times until the condition becomes false. Loops are of 2 types: entry-controlled and exit-controlled. 'C' programming provides us 1) while 2) do-while and 3) for loop.
- C has a comma operator, that basically combines two statements so that they can be considered as a single statement. About the only place this is ever used is in for loops, to either provide multiple initializations or to allow for multiple incrementations.
What Is Looping In Programming

Looping is one of the key concepts on any programming language. A block of looping statements in C are executed for number of times until the condition becomes false. Loops are of 2 types: entry-controlled and exit-controlled. 'C' programming provides us 1) while 2) do-while and 3) for loop.
Looping Statement In Shell Scripting
In computer programming, conditional loops or repetitive control structures are a way for computer programs to repeat one or more various steps depending on conditions set either by the programmer initially or real-time by the actual program.
A conditional loop has the potential to become an infinite loop when nothing in the loop's body can affect the outcome of the loop's conditional statement. However, infinite loops can sometimes be used purposely, often with an exit from the loop built into the loop implementation for every computer language, but many share the same basic structure and/or concept. The While loop and the For loop are the two most common types of conditional loops in most programming languages.
Types[edit]
The following types are written in C++, but apply to multiple languages.
While loop[edit]
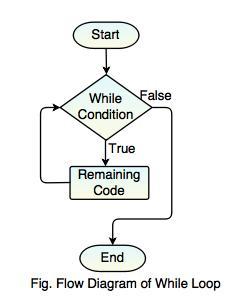
Checks condition for truthfulness before executing any of the code in the loop. If condition is initially false, the code inside the loop will never be executed. In PL/I this is a DO WHILE.. statement.
Do-While loop[edit]
Checks condition for truthfulness after executing the code in the loop. Therefore, the code inside the loop will always be executed at least once. PL/I implements this as a DO UNTIL.. statement.
For loop[edit]
A simplified way to create a while loop. Stellar phoenix video repair registration key free.
Initialization is executed just once before the loop. Condition evaluates the boolean expression of the loop. Statement is executed at the end of every loop.
So for example, the following while loop:
Could be written as the following for loop:
For-Each loop[edit]
A for-each loop is essentially equivalent to an iterator. It allows a program to iterate through a data structure without having to keep track of an index. It is especially useful in Sets which do not have indices. An example is as follows:
Examples[edit]

- An if statement can be followed by an optional else if.else statement, which is very usefull to test various conditions using single if.else if statement. When using if, else if, else statements there are few points to keep in mind.
- Oct 29, 2020 Looping is one of the key concepts on any programming language. A block of looping statements in C are executed for number of times until the condition becomes false. Loops are of 2 types: entry-controlled and exit-controlled. 'C' programming provides us 1) while 2) do-while and 3) for loop.
- C has a comma operator, that basically combines two statements so that they can be considered as a single statement. About the only place this is ever used is in for loops, to either provide multiple initializations or to allow for multiple incrementations.
What Is Looping In Programming
Looping is one of the key concepts on any programming language. A block of looping statements in C are executed for number of times until the condition becomes false. Loops are of 2 types: entry-controlled and exit-controlled. 'C' programming provides us 1) while 2) do-while and 3) for loop.
Looping Statement In Shell Scripting
In computer programming, conditional loops or repetitive control structures are a way for computer programs to repeat one or more various steps depending on conditions set either by the programmer initially or real-time by the actual program.
A conditional loop has the potential to become an infinite loop when nothing in the loop's body can affect the outcome of the loop's conditional statement. However, infinite loops can sometimes be used purposely, often with an exit from the loop built into the loop implementation for every computer language, but many share the same basic structure and/or concept. The While loop and the For loop are the two most common types of conditional loops in most programming languages.
Types[edit]
The following types are written in C++, but apply to multiple languages.
While loop[edit]
Checks condition for truthfulness before executing any of the code in the loop. If condition is initially false, the code inside the loop will never be executed. In PL/I this is a DO WHILE.. statement.
Do-While loop[edit]
Checks condition for truthfulness after executing the code in the loop. Therefore, the code inside the loop will always be executed at least once. PL/I implements this as a DO UNTIL.. statement.
For loop[edit]
A simplified way to create a while loop. Stellar phoenix video repair registration key free.
Initialization is executed just once before the loop. Condition evaluates the boolean expression of the loop. Statement is executed at the end of every loop.
So for example, the following while loop:
Could be written as the following for loop:
For-Each loop[edit]
A for-each loop is essentially equivalent to an iterator. It allows a program to iterate through a data structure without having to keep track of an index. It is especially useful in Sets which do not have indices. An example is as follows:
Examples[edit]
The following is a C-styleWhile loop. It continues looping while x does not equal 3, or in other words it only stops looping when x equals 3. However, since x is initialized to 0 and the value of x is never changed in the loop, the loop will never end (infinite loop).
The while loop below will execute the code in the loop 5 times. x is initialized to 0, and each time in the loop the value of x is incremented. The while loop is set up to stop when x is equal to 5.
Frequent bugs[edit]
Conditional loops are often the source of an Off by one error.
- C++ Basics
- C++ Object Oriented
- C++ Advanced
- C++ Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
Unlike for and while loops, which test the loop condition at the top of the loop, the do..while loop checks its condition at the bottom of the loop.
Example Of Looping Statement
A do..while loop is similar to a while loop, except that a do..while loop is guaranteed to execute at least one time.
Syntax
The syntax of a do..while loop in C++ is −
Notice that the conditional expression appears at the end of the loop, so the statement(s) in the loop execute once before the condition is tested.
If the condition is true, the flow of control jumps back up to do, and the statement(s) in the loop execute again. This process repeats until the given condition becomes false.
What Is Looping
Flow Diagram
Example
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
